intro
In the world of databases, PostgreSQL (often referred to as Postgres) is a highly popular open-source relational database management system known for its robustness and flexibility. Meanwhile, Docker is a platform that allows developers to build, ship, and run applications in a consistent environment. In this blog post, we will walk you through setting up PostgreSQL using Docker. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a PostgreSQL database running in a Docker container, ready for application development.
Setting up Postgres using Docker image
Before we begin, make sure that you have Docker installed on your system. If you don't, please install Docker first. You can download Docker for your operating system from the official Docker website. Once you have Docker installed, follow these steps to set up Postgres using Docker:
Step 1 - Pull the Postgres Docker image
The first step is to pull the Postgres Docker image from the Docker Hub repository, this is done by running the following command:
1
docker pull postgres
This command will download the latest version of the Postgres Docker image.
Step 2 - Create a Docker volume
Next, we need to create a Docker volume to persist our Postgres data, run the following command:
1
docker volume create postgres_data
The above command will create a Docker volume named postgres_data. This volume will be used to store our Postgres data even if the container is removed.
Step 3 - Run the Postgres Docker container
Now we can run the Postgres Docker container using the following command:
1
docker run --name postgres_container -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mysecretpassword -d -p 5432:5432 -v postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data postgres
The above command will create a container named postgres_container, set the environment variable POSTGRES_PASSWORD to mysecretpassword, map the container port 5432 to the host port 5432, and link the Docker volume postgres_data to the container directory /var/lib/postgresql/data.
Step 4 - Verify the Container is running
To verify that the Docker container is running, run the following command:
1
docker ps
This will list all the running Docker containers. You should see the postgres_container listed.
Step 5 - Connect to the Postgres database
To connect to the Postgres database, we will use a PostgreSQL client. If you don't have one installed, download and install DbVisualizer, a top-rated PostgreSQL client, then, once you have a client installed, connect to the database using the following details:
Host: localhost Port: 5432 Database: your database (in this case, the database is postgres) Username: your username (in this case, the username is also postgres) Password: your password (in this case, mysecretpassword)
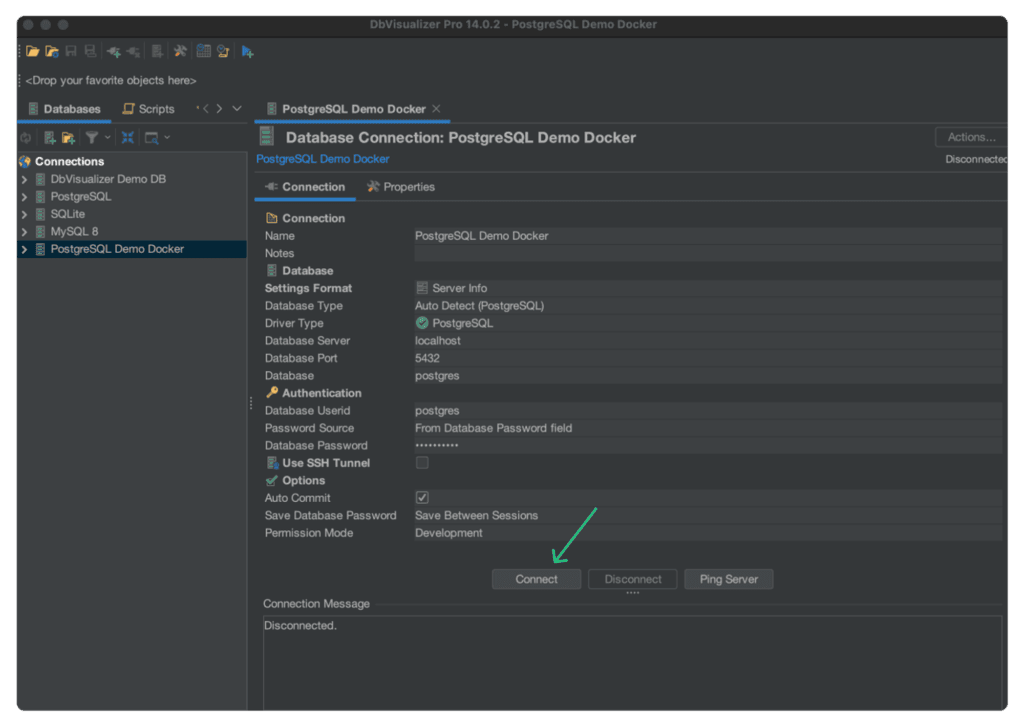
That's it! You have successfully set up PostgreSQL using Docker.
Benefits of using Postgres with Docker
Using Postgres with Docker has many benefits, some of them are listed here.
Easy to use
Setting up Postgres using Docker is very easy. You don't have to worry about installing and configuring PostgreSQL on your system. You can simply run a Docker container and start using PostgreSQL.
Isolated environment
Docker provides an isolated environment for running applications. This means that you can run Postgres in a container without worrying about affecting other applications on your system. It also means that you can easily switch between different versions of PostgreSQL without affecting other applications.
Easy to deploy
Deploying PostgreSQL with Docker is very easy. You can simply create a Docker image of your application and deploy it to any Docker-enabled environment. This means that you can easily deploy your PostgreSQL application to any cloud provider that supports Docker.
FAQ
What are the system requirements for running Postgres in Docker?
To run Postgres in Docker, you need:
How do I check if my Postgres container is running?
You can check the status of your Postgres container by running:
1
docker ps
This command lists all running containers. If your Postgres container is not running, you can start it with:
1
docker start postgres_container
How do I stop and remove the Postgres container?
To stop the container, run:
1
docker stop postgres_container
To remove the container, first stop it and then run:
1
docker rm postgres_container
How do I persist data when using Postgres in Docker?
To ensure data persistence, use a Docker volume when running your Postgres container. The example command in this guide includes:
1
-v postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
This ensures that even if the container is removed, your data remains in the volume postgres_data.
Can I access Postgres from an external application?
Yes, you can connect to your Postgres database from an external application using:
Host: localhost
Port: 5432
Username: postgres
Password: mysecretpassword
Ensure your firewall and Docker networking allow external connections if needed.
What happens if I restart my computer? Will my database persist?
Yes, if you used a volume (-v postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data), your database will persist. You may need to restart the container with:
1
docker start postgres_container
Conclusion
Setting up PostgreSQL using Docker is a straightforward process that offers many benefits, such as ease of use, environment isolation, and simplified deployment. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can quickly have a PostgreSQL database running in a Docker container, ready for development or deployment. We hope you found this tutorial helpful. Stay tuned to the DbVisualizer blog for more insights and tutorials. Happy coding!


